Identifying and working to resolve bottlenecks is key to a dairy’s reproductive program. The Reproductive Drill-Down Tool, created by Penn State Extension educators, was recently released to address this concern. Rebecca White of the Penn State Extension Dairy Team explains how this tool works and what it can do for dairy producers. Q: What is the web address? www.das.psu.edu/research-extension/dairy/pa-tool/identifying-bottlenecks-to-higher-dairy/
 Q: Why was it developed?
Q: Why was it developed?
WHITE : The Reproduction Drill-Down Tool was developed to provide a systematic approach to critically analyze the major factors affecting heat detection rate and conception rate.
Problem areas are identified to provide focus for discussions or talking points addressing reproductive performance on a dairy operation.
Q: Who should use it?
WHITE : Dairy consultants and extension educators.
Q: Is there a cost to use it?
WHITE : There is no cost to use the tool. To access the reproduction drill-down, click login on the main tool homepage and create a free membership.
Once logged in, the reproduction drill-down, as well as other tools, are accessible.
Q: What are some unique features?
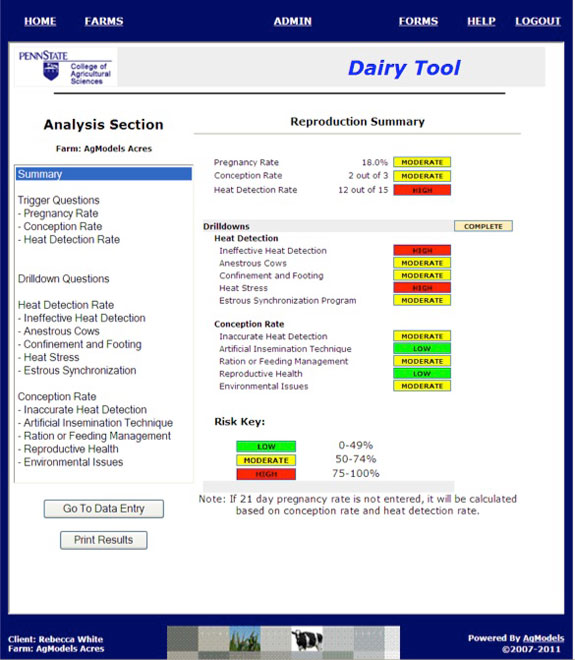
WHITE : The summary highlights areas of reproductive management that need improvement and can be quickly interpreted by a color-coding.
Each topic is highlighted with red, yellow or green indicating a high, medium or low risk, respectively, to reproductive performance.
Q: How does it work?
WHITE : The drill-down works by initially asking a series of “trigger questions” that indicate whether conception rate or heat detection or both are the greatest contributors to low pregnancy rates. Answers to the drill-down questions highlight the areas where changes need to be made.
The drill-down questions are divided into two categories – heat detection rate and conception rate – and then broken down further into specific areas:
• Ineffective heat detection
• Anestrous cows
• Confinement and footing
• Heat stress
• Estrous synchronization program
• Inaccurate heat detection
• Artificial insemination technique
• Ration or feeding management
• Reproductive health
• Environmental issues
Each area of reproduction management is assigned a “risk level” based on the answers chosen. Categories that are assigned a higher risk level indicate areas requiring attention to improve reproductive performance.
Q: Why is this important to understand or utilize?
WHITE : Achieving good 21-day pregnancy rates on a consistent basis is a crucial component of a profitable dairy enterprise. However, reproduction is affected by many factors, and consequently, evaluating a herd to identify the bottlenecks limiting reproductive performance is a challenge. PD

-
Dario Martinez
- Assistant Editor
- Email Dario Martinez






